Planck Telescope Qualification Model Test
18 March 2004
The structure of the Planck telescope has to remain dimensionally stable, maintaining the mirror positions with an accuracy better than 30 µm, over a wide temperature range. The qualification model of the telescope has recently been tested to correlate the thermoelastic model used in its design with actual performance.The frame of the Planck telescope qualification model, which is being constructed by Contraves Space AG of Zurich, was transported to the Cannes facility of Alcatel Space in order for videogrammetric measurements to be performed in vacuum and as close to operational temperatures as possible.
 |
 |
|
The telescope frame being unpacked from its shipping container. |
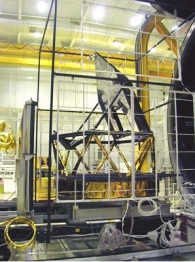
The telescope frame mounted on the test fixture using thermally isolating struts. |
The telescope will operate at about 55 K, its temperature reduced by thermal radiation to cold space, but it will be integrated and aligned at room temperature. It will be attached to the spacecraft's service module, operating at 300 K, by an intermediate structure made up of twelve struts that provide thermal conduction isolation. Three thermal shields will prevent thermal radiation from the service module reaching the telescope.
 |
 |
|
Telescope frame and test fixture mounted on the carriage which transports them into the test chamber. |
Carriage with telescope frame and videogrammetry equipment in the test chamber. |
For the test, the telescope frame was mounted on a test fixture which simulates the mechanical and thermal interfaces of the spacecraft service module. The mounting was made using the qualification model of thermally isolating intermediate structure. The telescope and test fixture were then placed in a vacuum chamber. The interface between the test fixture and the intermediate structure was maintained at 300 K while the telescope temperature was reduced to less than 90 K using cryogenic shrouds cooled with liquid nitrogen.
The chamber pressure during the vacuum part of the test was less than
Videogrammetric measurements were performed:
- At ambient temperature and pressure
- At ambient temperature, in vacuum
- During cooling
- At low temperature
- During warm up
- At ambient temperature, in vacuum
- At ambient temperature and pressure
The measurements were made with an accuracy of better than 30 µm to confirm the predictions of the thermoelastic model regarding the dimensional stability of the structure as the temperature varies.
