Microwave
| Wavelength range | m | 10-1 - 10-4 |
| Frequency range | Hz | 3×109 - 3×1012 |
|
Energy range |
eV | 10-5 - 10-2 |
 |
|
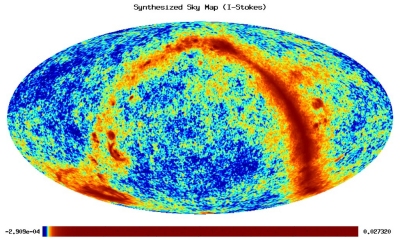
Synthesized map of the whole sky in microwave radiation as it will be observed by Planck. On top of the CMB, the emission from our galaxy, the Milky Way, is clearly visible as the curved red band across the image. |
ESA Missions
Planck
Planck's main objective is to observe the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) at unprecedented angular and temperature resolutions with observations covering the frequency range 27×109 to 1×1012 Hz.
Herschel
Next to the longer wavelength region of the infrared (called far infrared) Herschel will also observe in the submillimetre or microwave region of the spectrum. Its objectives include for example the study of galaxy formation in the early universe and their subsequent evolution and the study of stellar birth and interactions of stars with the interstellar medium.
Sources of Microwave radiation
The most well known source of microwave radiation is the Cosmic Microwave Background. This is the remnant energy of the Big Bang that permeates the Universe and has a temperature of about 2.73 K. The peak of the emission lies in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
