Interactive
Please note the content on this page is not maintained
Telescopes
 |
Resolving Power The ability to separate two objects on the night sky is determined by the resolving power of the eye, or instruments being used to observe the heavens. |
 |
Enlarging Power A telescope (special lens/mirrors system) increases the apparent visual size of the observed body. |
 |
Atmospheric Effects - Particulates Particulates in the atmosphere cause light to be scattered. This has two effects - firstly to diminish the brightness of the stars and secondly to increase local scattered light. |
 |
Atmospheric Effect - Heat The warmer the atmosphere the more turbulent it becomes. This means that the light path through the atmosphere is changing so objects appear to brighten and fade (twinkle). |
 |
Atmospheric Effects - Light Pollution Light given off from local sources (such as street lights) brightens the sky and makes it harder to see fainter objects. |
Space Travel
 |
Flight to the Moon A simple animation showing how a spacecraft transfers from orbit around the Earth to an orbit around the Moon |
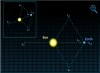 |
Lissajous Orbit The ESA Gaia mission will be placed in a Lissajous orbit at the second Lagrange point. |
The Galaxy
 |
3D Model of Milky Way An interactive 3D model of our galaxy that allows you to rotate, zoom in and out and select the objects to be viewed. |
 |
Measuring the Milky Way Explore the difference between Hipparcos data gathered after 1989 and that projected for Gaia. |
Physics
 |
Effect of Gravity on Light The illustration shows how light deflection depends on the mass and the size of a celestial body. |
Observing Stars
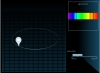 |
Radial Velocity via Doppler Effect The illustration shows Doppler's effect which is the change of frequency of a signal when the source of the signal moves either away from us or toward us. |
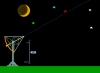 |
Sextant Early astronomers used the sextant to measure the positions of the stars. |
 |
Stellar Parallax This illustration shows how parallax affects our perception of the apparent position of a star near to us. |
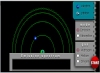 |
Spectroscopy The illustration demonstrates the formation mechanism for an emission spectrum and an absorption spectrum. |
Search for Planets
 |
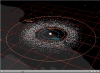
Solar System Formation A simulation showing how the soalr system formed. |
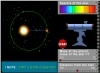 |
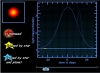
Dynamical Perturbations In this simulation, you see a hypothetical star system with one planet orbiting the star. |
 |
Gravitational Lensing Light rays traveling from the background star towards us pass very close to the second 'lensing' star, and the gravity of the latter bends the light path just as a lens system would. |
QT Movies
 |
Formation of Planets A short QuickTime movie that describes the formation of the planets. |
 |
Asteroid Belt A simple QuickTime movie that shows the positions and motions of asteroids located in the asteroid belt. |
Last Update: 4 May 2022
