Hubble and Spitzer Space Telescopes find building-block galaxies in early Universe [heic0714]
6 September 2007
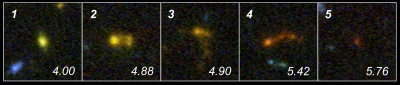
The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope and the NASA Spitzer Space Telescope have joined forces to discover nine of the smallest, faintest, most compact galaxies ever observed in the distant Universe. Blazing with the brilliance of millions of stars, each of the newly discovered galaxies is a hundred to a thousand times smaller than our Milky Way Galaxy.One of the conventional models for galaxy evolution predicts that small galaxies in the early Universe evolved into the massive galaxies of today by coalescing. Nine young building block galaxies initially detected by Hubble likely contributed to the construction of the Universe as we know it. "These are among the lowest mass galaxies ever directly observed in the early Universe" says Nor Pirzkal of the European Space Agency/Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI).
 |
|
Five of the nine compact galaxies in the Hubble Ultra Deep Field studied by Pirzkal et al [2007], with a redshift between 4.00 and 5.76 |
Pirzkal was surprised to find that the galaxies' estimated masses were so small. Hubble's cousin observatory, NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope was called upon to make precise determinations of their masses. The Spitzer observations confirmed that these galaxies are some of the smallest building blocks of the Universe.
These young galaxies offer important new insights into the Universe's formative years, just one thousand million years after the Big Bang. Hubble detected blue stars residing within the nine pristine galaxies. The youthful stars are just a few million years old and are in the process of turning lighter elements created right after the Big Bang (hydrogen and helium) into heavier elements. The stars have probably not yet begun to enrich the surrounding space with elemental products forged within their cores.
"While blue light seen by Hubble shows the presence of young stars, it is the absence of infrared light in the sensitive Spitzer images that was conclusive in showing that these are truly young galaxies without an earlier generation of stars," says Sangeeta Malhotra of Arizona State University in Tempe, USA, one of the investigators.
The galaxies were first identified by James Rhoads of Arizona State University, USA, and Chun Xu of the Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics in Shanghai, China. Three of the galaxies appear to be slightly disrupted – rather than being round-shaped, they appear stretched into tadpole-like shapes. This is a sign that they may be interacting and merging with neighbouring galaxies to form larger, cohesive structures.
 |
|
The Hubble Ultra Deep Field |
Notes for editors
The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA.
Pirzkal's main collaborators were Malhotra, Rhoads, Xu, and the GRism ACS Program for Extragalactic Science (GRAPES) team.
Image credit: NASA, ESA and N. Pirzkal (European Space Agency/STScI)
Contact
Nor Pirzkal
European Space Agency/Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, USA
Tel: 410-338-4879
E-mail: npirzkal stsci.edu
stsci.edu
Lars Lindberg Christensen
Hubble/ESA, Garching, Germany
Tel: +49-89-3200-6306
Cellular: +49-173-3872-621
E-mail: lars eso.org
eso.org
Ray Villard
Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, USA
Tel: +1-410-338-4514
E-mail: villard stsci.edu
stsci.edu
Whitney Clavin
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, USA
Tel: +1-818-354-4673
E-mail: whitney.clavin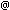 jpl.nasa.gov
jpl.nasa.gov

