ESA Science & Technology - News Archive
News archive
News archive
Data from the Visual Monitoring Camera (VMC) instrument onboard ESA's Mars Express is now available in the Planetary Science Archives (PSA). The data come from observations taken of Mars between 2007 to mid-2020, as well as of the release of the Beagle 2 lander in 2003, and are calibrated for scientific use.
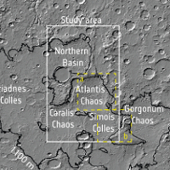
Two studies based on ESA's Mars Express observations of Jezero crater, the future landing site for NASA's 2020 Mars Perseverance rover, have shed light on how and when this intriguing area formed – and identified the regions most likely to reveal signs of ancient life.
In June, NASA's Curiosity rover reported the highest burst of methane recorded yet, but neither ESA's Mars Express nor the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter recorded any signs of the illusive gas, despite flying over the same location at a similar time.
In past decades, spacecraft have sent back huge amounts of complex data about Mars, providing a wealth of information about the planet. More than ever, the scientific community needs a way to sift through, compare, and analyse these data, prompting the development of two new tools for exploring the surface of the Red Planet.