No. 230 - Radio Science Investigations – Start of Occultation Campaign #10
Outbound quadrature manoeuvres
The spacecraft has been operating in outbound quadrature since 30 December 2010. Quadrature phases are periods of about five weeks during which the Sun-spacecraft-Earth angle is between 75° and 95°. They occur twice in every synodic period [see note 1] of Venus (584 days, or about 19 months), with an inbound quadrature phase ending 9 weeks before an inferior conjunction [see note 2] of Venus and an outbound quadrature phase starting 9 weeks after an inferior conjunction. This outbound quadrature phase started nine weeks after the inferior conjunction that occurred on 30 October 2010 and will last until 6 February 2011.
The design of Venus Express requires that only the +X and +Z faces of the spacecraft be exposed to solar illumination. During quadrature operation, the Earth-Sun-Venus geometry is such that the spacecraft has to be rotated 180 degrees to avoid illumination of the –X face. Two critical activities related to the management of solar illumination take place during this phase: biasing of the spacecraft attitude to prevent solar illumination of the Venus Monitoring Camera and swapping between the two high-gain antennas, which is accomplished during the rotation of the spacecraft about its Z-axis.
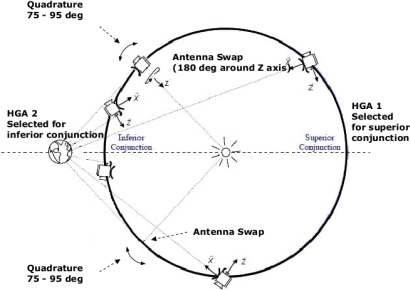 |
|
Schematic diagram showing antenna selection during quadrature operation. Credit: ESA |
VeRa Earth occultation campaign #10
The mission's tenth Earth occultation campaign began during this reporting period. These campaigns take place when the Earth is occulted by the disk of Venus; this occurs around the pericentre passages as seen from the spacecraft. Under these conditions unique measurements can be made to investigate the fine structure of the neutral atmosphere and ionosphere of Venus.
The occultation measurements are part of the Venus Express Radio Science Investigations (RSI) performed under the Venus Radio Science experiment (VeRa). For these investigations the VeRa team makes use of the radio links of the spacecraft's communications system. The spacecraft's High Gain Antenna (HGA) is pointed toward the Earth before the approach to occultation. The on-board ultra-stable oscillator is used to generate a very stable signal which is sent to Earth over the HGA simultaneously in the S-band and X-band. Just before and after the occultation the transmitted radio signal passes through the ionosphere and atmosphere of Venus. The effect that this has on the received signal gives valuable information on the characteristics of the atmosphere (such as temperature, density and pressure) as a function of altitude.
RSI occultation measurements were performed around pericentre on nine orbits in the reporting period. Two ground stations were used for receiving the spacecraft's radio signals on ground: the ESA deep space antenna at New Norcia (NNO) and the NASA Deep Space Network ground station at Canberra (CAN).
Summary of main activities
During the reporting period, routine mission operations were conducted using the ESA Cebreros ground station (CEB). A number of Cebreros communications passes were skipped or shortened at the request of the Venus Express Science Operations Centre (VSOC). Ground communications were switched from the secondary high-gain antenna (HGA2) to the primary antenna (HGA1) on 12 January 2011. Delta Differential One-way Ranging (DDOR) was performed on 16 January 2011 using the Cebreros and New Norcia (NNO) ground stations. Between 17 and 29 January 2011, RSI measurements were performed by observing the occultation of signals from the Venus Express spacecraft as it passed through orbital pericentre. A total of nine observations were performed, using the NASA Deep Space Network Canberra (CAN) and ESA New Norcia ground stations. RSI Occultation Campaign #10 will last until 23 March 2011.
| Main activities during reporting period | |||
|
MET |
Date |
DOY |
Main Activity |
|
MET = Mission elapsed time; DOY = Day of year | |||
| 1881 | 2-Jan-2011 | 2 | Shortened CEB communications pass. |
| 1882 | 3-Jan-2011 | 3 | Skipped pass. |
| 1883 | 4-Jan-2011 | 4 | Shortened CEB communications pass. |
| 1884 | 5-Jan-2011 | 5 | Shortened CEB communications pass. |
| 1885 | 6-Jan-2011 | 6 | Shortened CEB communications pass. |
| 1886 | 7-Jan-2011 | 7 | Shortened CEB communications pass. |
| 1887 | 8-Jan-2011 | 8 | Shortened CEB communications pass. |
| 1888 | 9-Jan-2011 | 9 | Shortened CEB communications pass. Telemetry bit rate set to 38 kbps before CEB pass. |
| 1889 | 10-Jan-2011 | 10 | Shortened CEB communications pass. |
| 1890 | 11-Jan-2011 | 11 | CEB communications pass. |
| 1891 | 12-Jan-2011 | 12 | CEB communications pass. High-Gain Antenna (HGA) swap (HGA2 –> HGA1) before CEB pass. Telemetry bit rate set to 228 kbps before CEB pass. |
| 1892 | 13-Jan-2011 | 13 | CEB communications pass. |
| 1893 | 14-Jan-2011 | 14 | Skipped pass. |
| 1894 | 15-Jan-2011 | 15 | CEB communications pass. |
| 1895 | 16-Jan-2011 | 16 | CEB communications pass. DDOR (NNO and CEB) before communications pass. |
| 1896 | 17-Jan-2011 | 17 | CEB communications pass. RSI Occultation over CAN around pericentre. |
| 1897 | 18-Jan-2011 | 18 | CEB communications pass. |
| 1898 | 19-Jan-2011 | 19 | CEB communications pass. RSI Occultation over CAN around pericentre. |
| 1899 | 20-Jan-2011 | 20 | CEB communications pass. |
| 1900 | 21-Jan-2011 | 21 | CEB communications pass. RSI Occultation over NNO around pericentre. |
| 1901 | 22-Jan-2011 | 22 | CEB communications pass. RSI Occultation over CAN around pericentre. |
| 1902 | 23-Jan-2011 | 23 | CEB communications pass. RSI Occultation over NNO around pericentre. |
| 1903 | 24-Jan-2011 | 24 | Skipped pass. |
| 1904 | 25-Jan-2011 | 25 | CEB communications pass. RSI Occultation over NNO around pericentre. |
| 1905 | 26-Jan-2011 | 26 | CEB communications pass. RSI Occultation over CAN around pericentre. |
| 1906 | 27-Jan-2011 | 27 | Skipped pass. |
| 1907 | 28-Jan-2011 | 28 | CEB communications pass. RSI Occultation over NNO around pericentre. |
| 1908 | 29-Jan-2011 | 29 | CEB communications pass. RSI Occultation over NNO around pericentre. |
At the end of the reporting period on 29 January 2011, Venus Express was 124.7 million kilometres from Earth. The one-way signal travel time was 416 seconds.
At the end of the reporting period, the final oxidizer mass was estimated to be 34.642 kilograms, and the final fuel mass estimate was 21.630 kilograms.
Payload Activities
| ASPERA | The instrument was regularly operated as part of the routine plan. |
| MAG | The instrument was regularly operated as part of the routine plan. |
| PFS | The instrument was not operated. |
| SPICAV | The instrument was regularly operated as part of the routine plan. |
| VMC | The instrument was regularly operated as part of the routine plan. |
| VeRa | Radio Science Investigation (RSI) occultation experiments were carried out via New Norcia (five passes) and NASA DSN Canberra (four passes). |
| VIRTIS | The instrument was regularly operated as part of the routine plan. |
Future Milestones
The spacecraft will exit outbound quadrature on 6 February 2011. Atmospheric Drag Experiment (ADE) #5 will start on 23 May 2011.
Notes
- The synodic period is the time between two successive identical configurations as seen from the Earth.
- A conjunction is the alignment of two Solar System bodies (in this case Venus and the Sun) so that they have the same longitude as seen from Earth. An inferior conjunction occurs when Venus is between the Sun and the Earth; superior conjunction refers to when Venus is on the opposite side of the Sun from Earth.
---
Legal disclaimer
This report is based on four ESOC mission operations reports, MOR #269 through MOR #272. Please see the copyright section of the legal disclaimer (bottom of this page) for terms of use.

