No. 261 - Continuation of the fifteenth Earth occultation season and the twenty-fourth solar eclipse season, implementation of automation of spacecraft passes and some non-routine operations
Cebreros ground station
All Cebreros ground station activities were nominal during this planning period. Routine maintenance was scheduled on 4 and 5 June, shortening the Earth communication slots on those days.
ESA ground station usage
The ESA tracking station network (ESTRACK) system of ground stations is spread across the globe. Interplanetary missions use ESTRACK's 35-m ground stations at New Norcia, Australia (Deep Space Antenna, DSA 1), Cebreros, Spain (DSA 2), and Malargüe, Argentina (DSA 3) – these three antennas form the European Deep Space Network (DSN). Venus Express normally only uses the ground station in Cebreros, Spain for data downlink and command uplink. The spacecraft's orbit around Venus is specifically designed so that Earth communications occur during normal working hours. This arrangement reduces costs by minimising personnel costs that would have been incurred due to out-of-hours support. As and when maintenance is required on the antenna or ground system, it is carried out during normal working hours, shortening the available communications slot with the spacecraft. In this planning period, maintenance slots were scheduled from 5:30 UTC to 10:30 UTC on 4 and 5 June, shortening the Earth communication slots from their normal eight to ten hours to the minimum acceptable duration of four hours on those days. For this reason, Venus Express operations also used the New Norcia ground station (for radio science observations) and the Malargüe ground station during the downtime scheduled on Cebreros.
In addition, starting on 17 June and continuing throughout this planning period, Venus Express had to share time with Mars Express on the Malargüe (MLG) station. This reduced the Venus Express data downlink in two ways:
- the Malargüe station is only visible from the spacecraft in the ascending branch of the Venus Express orbit, which is also the preferred period in which to obtain science data, and
- the downlink passes are shorter than normal while the available data rate remains constant, leading to less data being downlinked. Mars Express and Venus Express alternated short and long downlink periods on the Malargüe antenna. Under this arrangement, on one day Mars Express would be scheduled for a long pass of about 6.5 hours, and Venus Express would be scheduled for about 2.75 hours. Then on the next day, Mars Express would be scheduled for a short pass of about 2.25 hours, and Venus Express would be scheduled for a longer pass of about 7 hours. The short passes do not allow much data dumping, but they allow time for command uplinks and telemetry downlinks to ensure safe operations.
The Venus Express Mission Operations Centre also arranged for some data downlinks via the New Norcia ground station. The spacecraft was already using this ground station for radio science observations; in those orbits where other missions were not immediately using the station after Venus Express, the operations team extended their use of the ground station to include data downlinks in the available time. The station was reconfigured, from high-accuracy signal reception for science operations into a different baseband configuration that would accommodate routine operations for command uplink and telemetry downlink. On 17, 19 and 21 June, sufficient time was available on the station for this reconfiguration to be carried out and still leave time for command/ data transfer. In this way, the MOC were able to increase the data downlink volume on these days.
High accuracy spacecraft ranging
ESA's Cebreros and New Norcia ground stations were used for a Delta Differential One-way Ranging (delta-DOR, or DDOR) measurement at the start of the Cebreros communications pass on 15 June.
Delta-DOR measurements are carried out with the Venus Express spacecraft on a regular basis to support the accurate determination of the ephemeris for planet Venus that is maintained by NASA's Solar System Dynamics Group.
Continuation of the twenty-fourth eclipse season
Venus Express's twenty-fourth eclipse season continued throughout this reporting period. The Venus-Earth-spacecraft geometry was such that some Earth occultations and solar eclipses occurred simultaneously, after orbit pericentre.
Particular science observations are carried out during eclipse seasons: for further details, see the Scientific Focus section below and 'Science observations with Venus Express during an eclipse'.
Continuation of the Fifteenth Earth Occultation Season
The fifteenth Earth occultation season continued during this reporting period. Occultation observations were performed in every other orbit. The VeRa radio science occultation observations were alternated so that the SPICAV instrument could obtain measurements during eclipses of the Nitrogen Oxide concentrations in the atmosphere.
The spacecraft radio signal is received on Earth at the New Norcia antenna in western Australia, designated as antenna DSA-1. New Norcia is specifically used for radio science because it has the best viewing angle to Venus when the spacecraft is at pericentre (the Venus Express orbit is 24 hours long).
Spacecraft Event Time anomaly
The Venus Express spacecraft has a spacecraft event time issue in the solid state mass memory (SCET SSMM issue). This is due to a weakness in one of the memory's Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs). Whenever the Data Management System (DMS) sends a packet with a particular specific spacecraft event time (SCET) value, the writing of this packet into the SSMM fails. Additionally, the SSMM may then send a number of timeout events until some of the hardware resets. This means that no packet with the particular problematic SCET value can ever be stored in the SSMM.
The spacecraft manufacturer recommends that the data write operation from the DMS into the SSMM be suspended during these periods. The flight control team can predict when the particular spacecraft event time will occur. They then manually stop storage into the SSMM, and re-enable the storage into the SSMM after the known problematic period.
On 22 June, the spacecraft solid state mass memory (SSMM) was stopped for 15 minutes at 14:27:00 UTC. Only the magnetometer (MAG) was affected as it was the only instrument operating at the time, and none of the other instruments were writing data into the SSMM. That this period would be problematic was known well in advance. The team decided that it would rather bear the loss of 15 minutes of data than restart the instrument.
Automating spacecraft passes at the Mission Control Centre
Technology is allowing increased efficiency in many areas, and one of those areas is spacecraft operations at ESA's European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Darmstadt, Germany. Engineers have now completed the installation and testing of new software that allows the automation of routine daily contact with Venus Express. Beginning 2 June, a single spacecraft controller can oversee communications with multiple spacecraft, with human intervention required only if the spacecraft response differs from expected behaviour.
Thermal fuel gauging tests
Fuel gauging tests that help determine the exact amount of fuel and oxidizer remaining on board the spacecraft are currently underway on Venus Express. A number of these gauging tests were conducted over a few months, as and when time could be spared. The final testing in the current series has been completed; further actions must wait until the test data are processed by the contracted company.
For more information on the thermal gauging tests, see Venus Express Status Report no. 259.
Summary of main activities
The table below shows a chronology of the main spacecraft bus activities in the reporting period:
| Main activities during reporting period | |||
| ASPERA = Analyser of Space Plasma and Energetic Atoms; CEB = Cebreros; DOR = Differential One-way Ranging; DOY = Day of year; MET = Mission elapsed time; MLG = Malargüe; NNO = New Norcia; OCM = Orbit Correction Manoeuvre; SCET SMM = Spacecraft Event Time Solid State Memory Module | |||
|
MET (Day) |
Date | DOY | Main Activity |
| 2756 | 26-May-2013 | 146 | CEB communication pass. |
| 2757 | 27-May-2013 | 147 | CEB communication pass. |
| 2758 | 28-May-2013 | 148 | NNO occultation pass. CEB communication pass. |
| 2759 | 29-May-2013 | 149 | CEB communication pass. |
| 2760 | 30-May-2013 | 150 | NNO occultation pass. CEB communication pass. |
| 2761 | 31-May-2013 | 151 | CEB communication pass. |
| 2762 | 01-Jun-2013 | 152 | NNO occultation pass. CEB communication pass. |
| 2763 | 02-Jun-2013 | 153 | CEB communication pass. |
| 2764 | 03-Jun-2013 | 154 | CEB communication pass. NNO occultation pass. |
| 2765 | 04-Jun-2013 | 155 | CEB communication pass. CEB maintenance 5:30 UTC to 10:30 UTC. |
| 2766 | 05-Jun-2013 | 156 | CEB communication pass. NNO occultation pass. CEB maintenance 5:30 to 10:30 UTC. |
| 2767 | 06-Jun-2013 | 157 | CEB communication pass. |
| 2768 | 07-Jun-2013 | 158 | CEB communication pass. NNO occultation pass. |
| 2769 | 08-Jun-2013 | 159 | CEB communication pass. |
| 2770 | 09-Jun-2013 | 160 | CEB communication pass. |
| 2771 | 10-Jun-2013 | 161 | CEB communication pass. |
| 2772 | 11-Jun-2013 | 162 | Occultation pass at NNO. CEB communication pass. Successful patching of ASPERA software. |
| 2773 | 12-Jun-2013 | 163 | CEB communication pass. |
| 2774 | 13-Jun-2013 | 164 | Occultation pass at NNO. CEB communication pass. |
| 2775 | 14-Jun-2013 | 165 | CEB communication pass. |
| 2776 | 15-Jun-2013 | 166 | Occultation pass at NNO. Delta-DOR using CEB and NNO. CEB communication pass. |
| 2777 | 16-Jun-2013 | 167 | CEB communication pass. |
| 2778 | 17-Jun-2013 | 168 | NNO communication pass. MLG communication pass. Occultation observation with NNO. |
| 2779 | 18-Jun-2013 | 169 | MLG communication pass. |
| 2780 | 19-Jun-2013 | 170 | NNO communication pass. MLG communication pass. Occultation observation with NNO. |
| 2781 | 20-Jun-2013 | 171 | MLG communication pass. |
| 2782 | 21-Jun-2013 | 172 | NNO communication pass. MLG communication pass. Occultation observation with NNO. |
| 2783 | 22-Jun-2013 | 173 | MLG communication pass. SCET SSMM anomaly. |
At the end of the reporting period on 22 June, Venus Express was 231 million kilometres from Earth. The one-way signal travel time was 771 seconds. The final oxidizer mass was 18.235 kg and the final fuel mass was 11.152 kg.
Scientific focus
This reporting period falls under the ninety-third medium term planning period (MTP), which covered the period from 26 May to 22 June 2013. The fifteenth Earth occultation season and the twenty-fourth eclipse season continued throughout this period.
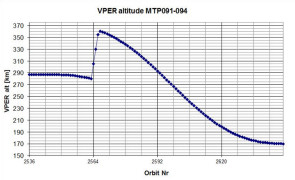
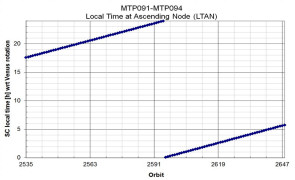
This reporting period was cold, so that pointing the +Z instrument face of the spacecraft at nadir did not expose any thermally sensitive faces of the spacecraft to the Sun, making more observations possible. The local time at ascending node changed from 23:45 hrs to 02:45 hrs. The data rate was still low, due to the relatively large distance between Earth and Venus.
During solar eclipses, when the spacecraft is in the shadow of the planet, the Venus Monitoring Camera (VMC) can make use of an infrared 'window' in the clouds to take low resolution images of the surface. A number of surface targets were accessible during this MTP. However, due to a focus on surface observations in the previous eclipse season, nightside observations of Nitrogen Oxide were given priority in this eclipse season.
The Venus-Earth-spacecraft geometry was such that the Earth occultation and solar eclipse period overlapped during this reporting period. The Solar Occultation at Infrared (SOIR) channel of the SPICAV instrument (Spectroscopy for Investigation of Characteristics of the Atmosphere of Venus) is specially designed to measure atmospheric absorption by observing the Sun through the Venusian atmosphere. Known as occultation observations, these can only be obtained during eclipse seasons, which is why they have high scientific priority during eclipse periods. In addition, the SPICAV team had planned Nitrogen Oxide measurements during the eclipses, and the Venus Radio science experiment (VeRa) team also planned to obtain radio science Earth occultation measurements at pericentre, during entry and exit from Earth occultations. Therefore the three types of observations (SPICAV/SOIR, SPICAV Nitrogen Oxide, VeRa occultation) were carried out in alternate orbits.
For further information, please see 'Science observations with Venus Express during an eclipse'.
Payload activities
| ASPERA |
The instrument was operated nominally as part of the routine plan. A software upgrade was carried out during this reporting period. The ASPERA instrument consists of three subsystems: the Neutral Particle Detector (NPD), the Neutral Particle Imager (NPI) and the Ion Mass Analyser (IMA). The ASPERA data rate scales with the number of particles it detects. Higher background levels mean that the instrument obtains more data, which can overflow the internal queue at times and lead to a loss of packets due to internal data buffer overflows. This is normally seen during high solar activity and it prevents accurate data analysis. To tackle this problem, the ASPERA IMA software has been upgraded to provide new functionality that enables automatic background level subtraction: The software will perform a subtraction from the data value for the background level which is calculated on-board to prevent packet loss. This change affects the IMA alone. The upgrade was completed smoothly on 11 June. The patch will be used in July for the first time. |
| MAG | The instrument was regularly operated nominally as part of the routine plan. |
| PFS | The instrument was not operated. |
| SPICAV |
The instrument was regularly operated nominally as part of the routine plan. On 4 June, a previously observed anomaly recurred on SPICAV. Some of the instrument data packets were generated with bad observation times. About 28 minutes of science data was lost due to these bad time tags. The instrument is turned on at the beginning of each observation, and then off at the end of the observation. The next time it was turned on, the problem had cleared and the time tags were correct. |
| VMC | The instrument was regularly operated nominally as part of the routine plan. |
| VeRa | The instrument was regularly operated nominally as part of the routine plan. |
| VIRTIS | The instrument was regularly operated nominally as part of the routine plan. |
Future milestones
- The twelfth Atmosphere Drag Experiment (ADE) campaign
- End of annual Cebreros extended maintenance.
- End of the twenty-fourth eclipse season End of the fifteenth occultation season
Legal disclaimer
This report is based on four ESOC mission operations reports, MOR 391 through MOR 394, as well as the MTP93 Master Science Plan. Please see the copyright section in the Terms and Conditions for this site.