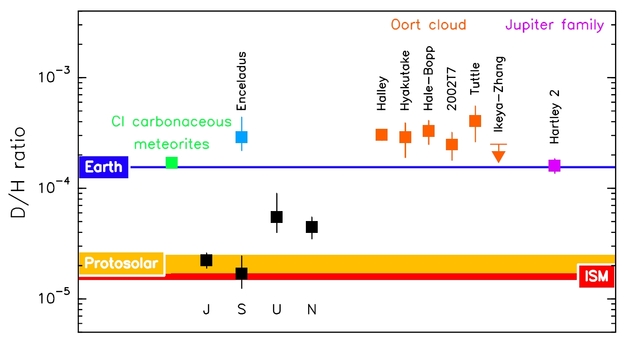
Deuterium-to-hydrogen ratio in the Solar System
Date: 05 October 2011
Satellite: Herschel
Depicts: Deuterium-to-hydrogen ratio in the Solar System
Copyright: Courtesy of Paul Hartogh, Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung
This graph displays the different values of the deuterium-to-hydrogen ratio (D/H) in water observed in various bodies in the Solar System.
The horizontal blue line shows the value of the ratio in Earth's oceans, which has been determined to be 1.56 ×10-4. The green square shows the value of the ratio measured in CI carbonaceous chrondrites, a class of meteorites found on Earth, which are believed to originate in the outer asteroid belt.
The six orange data points (five squares and an arrow indicating an upper limit) show the value of the D/H ratio in water observed in comets belonging to the Oort Cloud, which is twice as high as that of Earth-like water. The blue square indicates the value measured on Saturn's moon, Enceladus, which is also higher than that of Earth-like water.
The purple square on the right side of the graph shows the value of the D/H ratio in water observed in the Jupiter-Family comet 103P/Hartley 2, which is very similar to the value measured in Earth's oceans. This measurement is based on data acquired with the HIFI spectrometer on board Herschel in late 2010. As reported by Hartogh et al., 2011, these data represent the first evidence of Earth-like water detected in a comet.
The lower part of the graph shows the value of the D/H ratio measured in molecular hydrogen in the atmosphere of the giant planets of the Solar System (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune; black squares) and an estimate of the typical value in molecular hydrogen for the protosolar material (broad, yellow horizontal line) and in atomic hydrogen in the local interstellar medium (red horizontal line).
