Mercury Surface Element
Summary
The Mercury Surface Element (MSE), a simple short-lived probe, will study in-situ the physical properties of the surface. It will be deployed from the Magnetospheric Orbiter into an impact orbit to a high latitude landing site where the environmental conditions are less severe.
MSE can carry up to 7 kg of scientific hardware and additional, or alternative, instruments can be included in the model payload. Instruments visualised for MSE comprise a descent camera, a panorama camera, a seismometer, a magnetometer, an alpha-X-ray detector for chemical elements, and a package to assess the temperature, heat capacity, density and hardness of Mercury's 'soil'.
 |
|
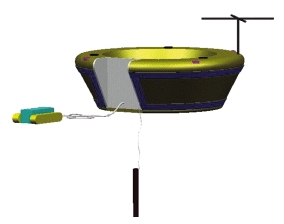
The MSE with the two deployment devices: the micro-rover (left) and the mole (bottom) |
A soil-penetrating device (MDD) and a micro-rover (MMR) are required for the deployment of some instruments. The MDD (mole) is derived from the Russian Mars programme and reaches depths of several metres in a regolith. A rover attached to a tether can deploy instruments at selected sites several metres away from the lander.
Table of instruments
| Acronym | Instrument | Deployment |
| AXS | Alpha X-ray spectrometer | By Mole |
| HP³ | Heat flow and physical properties package | By Micro-rover |
| SEISMO | Seismometer | None |
| CLAM-D | Descent camera | None |
| CLAM-S | Surface camera | None |
| MLMAG | Mercury lander magnetometer | None |
| MDD | Mole deployment device | - |
| MMR | Mercury micro-rover | - |
Instrument objectives
| HP³ | AXS | CLAM-D | CLAM-S | MLMAG | SEISMO | |
| Morphology | X | X | ||||
| Structure | X | X | X | |||
| Composition | X | X | ||||
| Mineralogy | X | X | X |
The two deployment devices MDD and MMR will deploy the HP³ and AXS instrument respectively.
