Herschel-HIFI unveils precursors of life-enabling molecules in Orion Nebula
4 March 2010
ESA's Herschel Space Observatory has revealed the chemical fingerprints of potential life-enabling organic molecules in the Orion Nebula, a nearby stellar nursery in our Milky Way galaxy. This detailed spectrum, obtained with the Heterodyne Instrument for the Far Infrared (HIFI) - one of Herschel's three innovative instruments - demonstrates the gold mine of information that Herschel-HIFI will provide on how organic molecules form in space.
 |
|
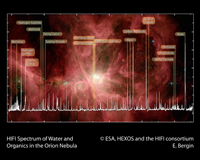
HIFI spectrum of water and organics in the Orion Nebula. Credit: ESA, HEXOS and the HIFI consortium |
By clearly identifying the lines associated with the more common molecules, astronomers can then begin to tease out the signature of particularly interesting molecules that are the direct precursors to life-enabling molecules. A characteristic feature of the Orion spectrum is the spectral richness: among the molecules that can be identified in this spectrum are water, carbon monoxide, formaldehyde, methanol, dimethyl ether, hydrogen cyanide, sulphur oxide, sulphur dioxide and their isotope analogues. It is expected that new organic molecules will also be identified.
"This HIFI spectrum, and the many more to come, will provide a virtual treasure trove of information regarding the overall chemical inventory and on how organics form in a region of active star formation. It harbours the promise of a deep understanding of the chemistry of space once we have the full spectral surveys available," said Edwin Bergin of the University of Michigan, principal investigator of the HEXOS Key Programme on Herschel.
Unprecedented high resolution
 |
|
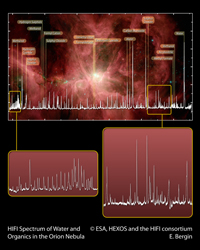
HIFI spectrum of the Orion Nebula showing detail for selected regions. Credit: ESA, HEXOS and the HIFI consortium |
"HIFI's unprecedented high resolution and stability allows us to construct very detailed models of the density and temperature structure of star-forming clouds," said Tom Phillips of the California Institute for Technology. "This view allows us to pierce the veil of star formation and more directly study the chemistry associated with the birth of stars, planets, and in some sense, life."
The spectrum was obtained only one month after HIFI resumed operations on-board Herschel. In August 2009, HIFI experienced an unexpected voltage spike in the electronic system, probably caused by a high-energy cosmic particle, resulting in the instrument shutting down. The mission team studied the problem and developed a solution that prevents harmful side-effects of this type of event. On 14 January, 2010, HIFI was successfully switched back on using its spare electronics and restarted a sequence of testing and verification, ahead of science observations commencing on 28 February. It now rejoins the other two Herschel instruments, SPIRE and PACS, in their exploration of the far-infrared Universe.
Notes for editors
Herschel is an ESA space observatory with science instruments provided by European-led Principal Investigator consortia, with important participation from NASA.
HIFI, a high resolution spectrometer was designed and built by a nationally-funded consortium led by SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research. The consortium includes institutes from France, Germany, USA, Canada, Ireland, Italy, Poland, Russia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and Taiwan.
Identification of the many spectral features visible in the Orion spectrum with transitions of particular molecular species requires sophisticated molecular spectroscopy databases, which collect the results from many years of laboratory spectroscopy work. The assignments for this HIFI spectrum were made using the Cologne Database of Molecular Spectroscopy (CDMS) and an equivalent database maintained at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
For more information please contact:
Göran Pilbratt, Herschel Project Scientist
Research and Scientific Support Department
Science and Robotic Exploration Directorate, ESA, The Netherlands.
Email: gpilbratt rssd.esa.int
rssd.esa.int
Phone: +31-71-565-3621
Frank Helmich, Principal Investigator for HIFI
SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research, The Netherlands.
Email: F.P.Helmich sron.nl
sron.nl
Phone: +31-6-49423644

