Extragalactic
Evolving galaxies
Having ISO in space gave astronomers special opportunities to study the history of galaxies. By detecting infrared wavelengths that are hard to observe from the Earth, ISO has picked out very clearly the galaxies that are evolving most rapidly via periods of intensive starmaking. ISO has also detected infrared galaxies powered by active galactic nuclei.
 |
|
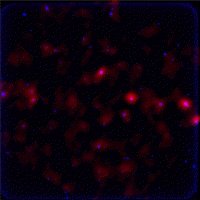
Starbursts in distant galaxies observed by ISO (red) and by ground-based infrared observation (blue). Credits: ISOCAM, Univsersity of Hawaii and Y. Taniguchi et al. |
The farthest known galaxy observed by ISO is a quasar called BR 1202-0725, dating from a time when the Universe was less than one tenth of its present age. Already it is dusty, indicating that star birth and death had ocurred by this early stage.
"The disks tell us that the system at least made small bodies, so it is likely that it also made planets," said Harm Habing of Leiden University in the Netherlands. "Our statistical study reveals that 50 percent of all young stars have these debris disks. ISO is breaking the ground for projects that will go in search of planets, even Earth-like planets, in the far future."