Titan Coverage by Cassini Radar Mapper
Date: 25 October 2005
Satellite: Cassini
Copyright: NASA/JPL
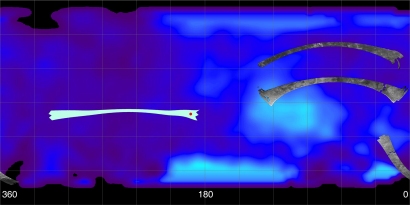
This map of Saturn's moon Titan shows the location of the upcoming 28 October 2005 Titan flyby, and the areas mapped so far by the Cassini Radar Mapper using its Synthetic Aperture Radar imaging mode. Longitudes are labeled at the bottom of the map.
The radar swaths are superimposed on a false-color image made from observations by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope.
The far left image shows the location of the radar swath for the upcoming 28 October flyby. The location of the Huygens landing site is marked in red. The overlap between the Huygens data and the radar data will give new clues to the nature of the surface seen by the Huygens probe, which landed on Titan in January 2005.
On the top right is the radar swath from the first Titan flyby, on 26 October 2004. The middle swath is from the second radar pass of Titan, on 15 February 2005 (near-equatorial). The 26 October swath is about 4500 kilometres long, extending from 133 degrees west longitude and 32 degrees north latitude through 12 degrees west and 29 degrees north. The February swath is centred at approximately 30 degrees north and 70 degrees west. The spatial resolution of the radar images ranges from about 300 metres per pixel to about 1.5 kilometres per pixel. The bottom right swath shows the strip acquired during the third radar pass, on 7 September 2005, close to Titan's south pole. The swath is centred at 12 degrees west and 51 degrees south, with similar spatial resolution to the previous two.
These first three radar passes revealed a variety of geologic features, including impact craters, wind-blown deposits, channels, and cryovolcanic features.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency.
