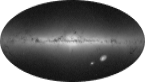
Gaia's new data takes us to the Milky Way's anticentre and beyond
3 December 2020
The motion of stars in the outskirts of our galaxy hints at significant changes in the history of the Milky Way. This and other equally fascinating results come from a set of papers that demonstrate the quality of ESA's Gaia Early third Data Release (EDR3), which is made public today.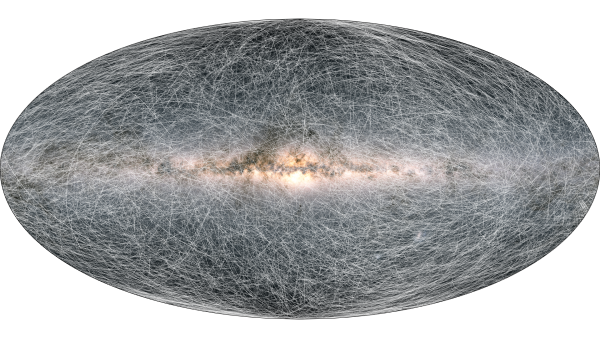 |
| Gaia's stellar motion for the next 400 thousand years. Credit: ESA/Gaia/DPAC, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO. Acknowledgement: A. Brown, S. Jordan, T. Roegiers, X. Luria, E. Masana, T. Prusti and A. Moitinho |
Astronomers from the Gaia Data Processing and Analysis Consortium (DPAC) saw the evidence of the Milky Way's past by looking at stars in the direction of the galaxy's 'anticentre'. This is in the exact opposite direction on the sky from the centre of the galaxy.
The results on the anticentre come from one of the four 'demonstration papers' released alongside the Gaia data. The others use Gaia data to provide a huge extension to the census of nearby stars, derive the shape of the Solar System's orbit around the centre of the galaxy, and probe structures in two nearby galaxies to the Milky Way. The papers are designed to highlight the improvements and quality of the newly published data.
What's new in EDR3?
Gaia EDR3 contains detailed information on more than 1.8 billion sources, detected by the Gaia spacecraft. This represents an increase of more than 100 million sources over the previous data release (Gaia DR2), which was made public in April 2018. Gaia EDR3 also contains colour information for around 1.5 billion sources, an increase of about 200 million sources over Gaia DR2. As well as including more sources, the general accuracy and precision of the measurements has also improved.
"The new Gaia data promise to be a treasure trove for astronomers," says Jos de Bruijne, ESA's Gaia Deputy Project Scientist.
 |
| The colour of the sky from Gaia's Early Data Release 3. Credit: ESA/Gaia/DPAC; CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO. Acknowledgement: A. Moitinho. |
To the galactic anticentre
The new Gaia data have allowed astronomers to trace the various populations of older and younger stars out towards the very edge of our galaxy – the galactic anticentre. Computer models predicted that the disc of the Milky Way will grow larger with time as new stars are born. The new data allow us to see the relics of the 10 billion-year-old ancient disc and so determine its smaller extent compared to the Milky Way's current disc size.
The new data from these outer regions also strengthen the evidence for another major event in the more recent past of the galaxy.
The data show that in the outer regions of the disc there is a component of slow-moving stars above the plane of our galaxy that are heading downwards towards the plane, and a component of fast-moving stars below the plane that are moving upwards. This extraordinary pattern had not been anticipated before. It could be the result of the near-collision between the Milky Way and the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy that took place in our galaxy's more recent past.
The Sagittarius dwarf galaxy contains a few tens of millions of stars and is currently in the process of being cannibalised by the Milky Way. Its last close pass to our galaxy was not a direct hit, but this would have been enough so that its gravity perturbed some stars in our galaxy like a stone dropping into water.
Using Gaia DR2, members of DPAC had already found a subtle ripple in the movement of millions of stars that suggested the effects of the encounter with Sagittarius sometime between 300 and 900 million years ago. Now, using Gaia EDR3, they have uncovered more evidence that points to its strong effects on our galaxy's disc of stars.
"The patterns of movement in the disc stars are different to what we used to believe," says Teresa Antoja, University of Barcelona, Spain, who worked on this analysis with DPAC colleagues. Although the role of the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy is still debated in some quarters, Teresa says, "It could be a good candidate for all these disturbances, as some simulations from other authors show."
Measuring the Solar System's orbit
 |
| Measuring the acceleration of the Solar System with Gaia. Credit: ESA/Gaia/DPAC; CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO. Acknowledgement: S. Jordan, T. Sagristà and Klioner et al (2020) |
The history of the galaxy is not the only result from the Gaia EDR3 demonstration papers. DPAC members across Europe have performed other work to demonstrate the extreme fidelity of the data and the unique potential for unlimited scientific discovery.
In one paper, Gaia has allowed scientists to measure the acceleration of the Solar System with respect to the rest frame of the Universe. Using the observed motions of extremely distant galaxies, the velocity of the Solar System has been measured to change by 0.23 nm/s every second. Because of this tiny acceleration the trajectory of the Solar System is deflected by the diameter of an atom every second, and in a year this adds up to around 115 km. The acceleration measured by Gaia shows a good agreement with the theoretical expectations and provides the first measurement of the curvature of the Solar System's orbit around the galaxy in the history of optical astronomy.
A new stellar census
Gaia EDR3 has also allowed a new census of stars in the solar neighbourhood to be obtained. The Gaia Catalogue of Nearby Stars contains 331 312 objects, which is estimated to be 92 percent of the stars within 100 parsecs (326 light years) of the Sun. The previous census of the solar neighbourhood, called the Gliese Catalogue of Nearby stars, was carried out in 1957. It possessed just 915 objects initially, but was updated in 1991 to 3803 celestial objects. It was also limited to a distance of 82 light years: Gaia's census reaches four times farther and contains 100 times more stars. It also provides location, motion, and brightness measurements that are orders of magnitude more precise than the old data.
Beyond the Milky Way
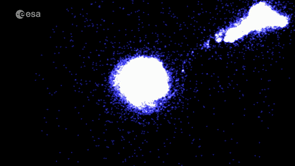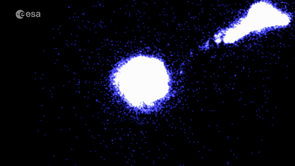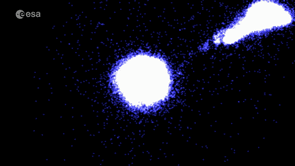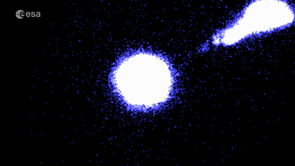 |
| Bridge of stars between the Magellanic clouds. Credit: ESA/Gaia/DPAC; CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO. Acknowledgements: S. Jordan, T. Sagristà, X. Luri et al (2020) |
A fourth demonstration paper analysed the Magellanic Clouds: two galaxies that orbit the Milky Way. Having measured the movement of the Large Magellanic Cloud's stars to greater precision than before, Gaia EDR3 clearly shows that the galaxy has a spiral structure. The data also resolve a stream of stars that is being pulled out of the Small Magellanic Cloud, and hints at previously unseen structures in the outskirts of both galaxies.
At 12:00 CET on 3 December, the data produced by the many scientists and engineers of the Gaia DPAC Consortium become public for anyone to look at and learn from. This is the first of a two-part release; the full Data Release 3 is planned for 2022.
"Gaia EDR3 is the result of a huge effort from everyone involved in the Gaia mission. It's an extraordinarily rich data set, and I look forward to the many discoveries that astronomers from around the world will make with this resource," says Timo Prusti, ESA's Gaia Project Scientist. "And we're not done yet; more great data will follow as Gaia continues to make measurements from orbit."
For more information, please contact:
Media Relations
Email: media![]() esa.int
esa.int