Herschel extreme lensing line observations: dynamics of two strongly lensed star-forming galaxies near redshift z=2
Publication date: 30 April 2014
Authors: Rhoads, J.E., et al.
Journal: The Astrophysical Journal
Volume: 787
Issue: 1
Year: 2014
Copyright: © 2014. The American Astronomical Society
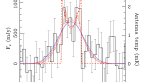
We report on two regularly rotating galaxies at redshift z ~ 2, using high-resolution spectra of the bright [C II] 158 μm emission line from the HIFI instrument on the Herschel Space Observatory. Both SDSS090122.37+181432.3 ("S0901") and SDSSJ120602.09+514229.5 ("the Clone") are strongly lensed and show the double-horned line profile that is typical of rotating gas disks. Using a parametric disk model to fit the emission line profiles, we find that S0901 has a rotation speed of vsin (i) ~ 120 ± 7 km s-1 and a gas velocity dispersion of sigmag < 23 km s-1 (1 sigma). The best-fitting model for the Clone is a rotationally supported disk having vsin (i) ~ 79 ± 11 km s-1 and sigmag 4 km s-1 (1 sigma). However, the Clone is also consistent with a family of dispersion-dominated models having sigmag = 92 ± 20 km s-1. Our results showcase the potential of the [C II] line as a kinematic probe of high-redshift galaxy dynamics: [C II] is bright, accessible to heterodyne receivers with exquisite velocity resolution, and traces dense star-forming interstellar gas. Future [C II] line observations with ALMA would offer the further advantage of spatial resolution, allowing a clearer separation between rotation and velocity dispersion.
Link to publication