How to form a SMART team to explore the Moon
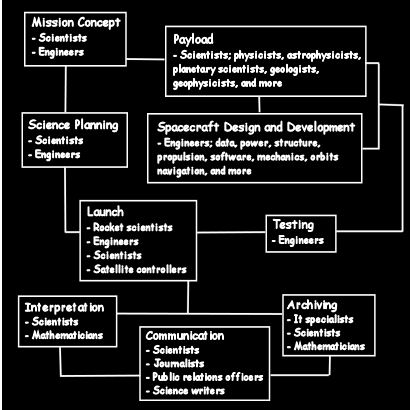
This schematic is an inexhaustive list of possible professions that are called upon at different phases of a mission. In addition there are support professions, such as project controllers, secretarial staff, documentalists, IT support, management, administration and more at almost every stage.
Designing a mission
Before a spacecraft can be built or even designed it needs to have a purpose. SMART-1 was first conceived in 1997. At that time a small team of experts were given the task to decide what the aims and objectives of the mission should be. The aim of SMART-1 was to test new technology whilst on a journey to the Moon. Designing and launching a spacecraft takes time and money and so upon reaching the Moon, and having completed the technology demonstration aspect of the mission, it was decided that SMART-1 one should also undertake some scientific investigations.
What experts are needed?
Within the team responsible for the task of seeing the mission come to fruition someone with experience of developing a space mission is needed to lead and guide the project overall. Engineers are required to bring their knowledge of materials, power, electronics, communications, mechanics and propulsion. To balance the technology with the science the mission will undertake when it reaches the Moon scientists are needed with knowledge of, for example physics, geology and space science. All space missions benefit from some of the people working on them having experience, however a younger generation are also necessary as they can bring new, fresh ideas into the project and are also likely to have the most up-to-date knowledge of new technologies.
Designing and building the spacecraft

Once the concept of a mission is agreed upon, the next step is to work out how it will get there and what it needs to make sure all the objectives are met. A number of different teams are required to work on each small element of the mission: such has how it will travel from the Earth to the Moon once it has been launched, and what science instruments are needed to obtain the data that is required. Once the spacecraft is launched it will need to send data back to Earth about the how the new technologies are working and the information the science instruments are taking.
Bringing a mission together
With many specialist teams working on different aspects of the project one of the challenging things to do is make sure that it will all fit together and work when it is completed and that everyone will be finished on time and within budget.
This means that someone has to be responsible for making sure that all teams keep to the schedule that was outlined at the beginning of the project. Communication is extremely important and so teams are asked to report on their portion of the project, therefore another important role is a person who ensures that everything that is taking place is documented properly.
Once a spacecraft is launched on its way to the Moon it is not possible to send someone to fix it should a problem occur, so throughout the process of building the spacecraft it is necessary for somebody to check that all is completed to a high standard and that it is of the right quality to endure launch and the harsh environment of space.
Launching a spacecraft
 |
Mission accomplished
The SMART-1 mission ran from its conception in 1997 until its planned impact onto the lunar surface in 2006.
Successful teamwork amongst so many people who are often located in different countries across Europe is challenging. Individual teams have their own personalities and methods, and are often working under pressure and time constraints. In order for all of these elements to be brought together these diverse teams must communicate effectively and remain motivated throughout the project lifetime. This is a significant challenge, requiring effective management. As those more experienced move on and leave the mission there must be a new generation ready to take their place.

