Euclid dark Universe mission ready to take shape
17 December 2015
Euclid, ESA's dark Universe mission, has passed its preliminary design review, providing confidence that the spacecraft and its payload can be built. It's time to start 'cutting metal'."This is really a big step for the mission," says Giuseppe Racca, Euclid's project manager. "All the elements have been put together and evaluated. We now know that the mission is feasible and we can do the science."
 |
| Artist's impression of the Euclid spacecraft. Credit: ESA/C. Carreau |
First proposed to ESA in 2007, Euclid was selected as the second medium-class mission in the Cosmic Vision programme in October 2011. Italy's Thales Alenia Space was chosen as the prime contractor in 2013.
Since then, the mission's design has been studied and refined. This has involved a wide range of detailed technical designs, in addition to building and testing key components.
The outcome of Euclid's recent review was positive, opening the door to the industrial contractors and external instrument teams building the spacecraft and payload for real. Airbus Defence & Space in France will deliver the complete payload module incorporating a 1.2 m-diameter telescope feeding the two science instruments being developed by the Euclid Consortium.
"This is a major milestone for us. Everyone is now ready to start cutting metal," says René Laureijs, Euclid's project scientist.
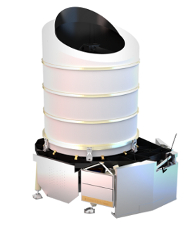 |
|
| Drawings of the Euclid payload module: (left) exterior view showing the baffle and (right) interior view showing the telescope. Credit: Airbus Defence & Space | |
On the scientific side, this review checked that the mission can indeed deliver the required data. The combined performance of the spacecraft, telescope and instruments shows that the data returned over the six-year mission will achieve the objectives.
Euclid is designed to give us important new insights into the 'dark side' of the Universe, namely 'dark matter' and 'dark energy', both key components of the current model for the formation and evolution of the Universe.
Observations made over recent decades reveal that less than 5% of the matter in the Universe is in the form of normal atoms, while a much larger amount of dark matter is inferred from measurements including the rotation speeds of galaxies. This matter acts through gravity, but is invisible.
Dark energy, on the other hand, is invoked to explain the finding that the expansion of the Universe is accelerating.
Although they are thought to make up the majority of the matter and energy in the Universe, dark matter and dark energy cannot be seen. Instead, their presence is inferred by the movement of galaxies, the shape of galaxies, their distribution in space, and the rate of the Universe's expansion as traced by the galaxies.
By mapping the shapes, positions and movements of two billion galaxies across more than a third of the sky, Euclid will provide astronomers with an unprecedented wealth of data to analyse.
The unrivalled accuracy of its measurements will allow them to close in on the properties and behaviour of dark matter and dark energy. This, in turn, will put constraints on the theoretical properties of what these two unseen components of the Universe may be.
With Euclid's preliminary design review now safely passed, the next major milestone comes in two years at the critical design review.
At this point, the major hardware components will have been built and tested. If all goes well, Euclid will then be assembled.
After this, Euclid will be ready for launch in December 2020 on a Soyuz rocket from Europe's Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana.
Notes for Editors
Euclid is an ESA survey mission to investigate the nature of dark matter and dark energy. It was selected as the second Medium-class mission in ESA's Cosmic Vision programme in October 2011 and formally adopted in June 2012. The mission will be launched in 2020 and will orbit around the Sun-Earth L2 point located 1.5 million km from Earth. Science and spacecraft operations will be conducted by ESA.
The prime contractor is Italy's Thales Alenia Space, who lead the construction of Euclid. Airbus Defence & Space in France will deliver a fully integrated payload module incorporating a 1.2 m-diameter telescope feeding the mission's two state-of-the art science instruments – a visible-light camera and a near-infrared camera/spectrometer – which are being developed by the Euclid Consortium. Together over a 6-year mission, they will measure the 3D distribution of two billion galaxies, the dark matter associated with them, and the influence of dark energy via the weak lensing and baryon acoustic oscillation techniques.
More than 1000 scientists from over 100 institutes form the Euclid Consortium building the instruments and participating in the scientific harvest of the mission. The consortium comprises scientists from 14 European countries: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Romania, Spain, Switzerland, and the UK. It also includes a number of US scientists, including 40 nominated by NASA, in return for hardware contributions to the mission.
For further information, please contact:
Markus Bauer
ESA Science and Robotic Exploration Communication Officer
Email: markus.bauer@esa.int
Tel: +31 71 565 6799
Giuseppe Racca
ESA Euclid Project Manager
Email: giuseppe.racca@esa.int
René Laureijs
ESA Euclid Project Scientist
Email: rene.laureijs@esa.int

.jpg)