Rosetta Second Earth Swing-by
12 November 2007
In the evening of 13 November, at 20:57 UTC, the Rosetta spacecraft returns to Earth for a second time after its launch in March 2004. The spacecraft will perform its second Earth swing-by which is part of a series of gravity assists required to put the spacecraft on an intercept course with comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko.Updates on the progress of the flyby can be found on the ESA Rosetta Swing-by site.
 |
|
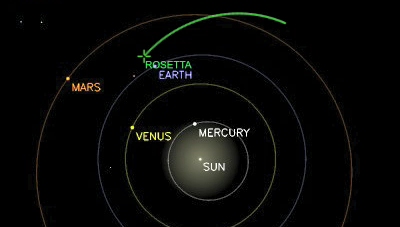
Position of inner Solar System planets and Rosetta's orbit (green) as it approaches the Earth for a second swing-by. (click for animation) |
| Launch |
2 March 2004 |
| First Earth gravity assist |
4 March 2005 |
| Mars gravity assist |
25 February 2007 |
| Second Earth gravity assist |
13 November 2007 |
| Third Earth gravity assist | 13 November 2009 |
|
Dates of Launch and Gravity Assists |
|
This second Earth swing-by occurs nearly 9 months after the Mars swing-by in February 2007 which slowed down Rosetta to direct it back into the inner Solar System towards Earth. The second Earth swing-by, plus the third Earth swing-by in two years time, will be used to increase Rosetta's velocity and provide it with the energy needed to journey out to nearly the orbit of Jupiter to rendez-vouz with comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko.
Swing-by Details
 |
|
View of Earth around closest approach (click for animation) |
Rosetta will swing by the Earth at a distance of 5301 km (compared to Earth's equatorial diameter of ~12 760 km), with closest approach at 20:57 UTC. At that time the spacecraft will be over the Pacific Ocean, south-west of Chile, at 74° 35' W, 63° 46' S. It's velocity relative to Earth will be 45 000 kmh-1 (12 500 ms-1).
During the swing-by, the highest priority will be given to spacecraft operations, as the manoeuvre is critical for the success of the overall mission. However, a few instruments both on the Rosetta orbiter and the Philae lander are and will be activated (see also the Rosetta status report from 12 November) for calibration, scientific measurements and imaging purposes. Observations of the Earth-Moon system will take place for about two weeks around closest approach, from 7 November, 00:00 UTC, until 20 November, 14:00 UTC.
Planned Science Activities
On the swing-by incoming and outgoing trajectory Rosetta will be in unfavourable solar illumination conditions, with thermal constraints for pointing, resulting in only limited time slots for the instruments to be safely used.
Each observation by the instruments that require pointing will start at the end of a slew manoeuvre that will orient the spacecraft correctly. A few instruments (ROMAP, RPC, SREM and Radio Science) do not require pointing to be operated.
Around closest approach, imaging by Rosetta's navigation camera is also foreseen, on a non-interference basis with OSIRIS and VIRTIS observations.
Scientific objectives
-
ALICE - orbiter's UV imaging spectrometer
Spectra of illuminated Earth for calibration purposes.
Spectra of illuminated Moon for calibration purposes. -
ROMAP - lander's magnetometer
Measurements of the Earth magnetosphere. -
RPC - orbiter's plasma consortium
Measurements of the Earth magnetosphere. In the case of RPC the measurements are also used for calibration purposes. -
MIRO - orbiter's microwave experiment
Earth and Moon observations for calibration purposes.
Earth observation around closest approach to test the 'asteroid mode sequence': ensure that the microwave radiation emitted by the 4 volatile molecular species MIRO is to study at the asteroids Steins and Lutetia will be in the bandwidth of the instrument (considering the Doppler shift due to the fact that the spacecraft is first approaching and then flying away from the target). -
RSI - orbiter's radio science investigation
Investigation of anomalous acceleration during swing/fly-bys. -
SREM - radiation monitor experiment
Measurements of Earth's radiation belt. -
OSIRIS - orbiter's Optical, Spectroscopic, and Infrared camera
Earth night-side pointing: includes imaging of urban regions in Asia, Africa and Europe at night (WAC) and a search for shooting stars from space (Rosetta will pass close to the Leonids clouds).
Lunar disk spectro-photometry.
Distant images of the Earth-Moon system when both are in the field of view of the Wide Angle Camera (WAC). -
VIRTIS - orbiter's visual and infrared mapping spectrometer
Study of fluorescence emission of CO2 and O2 through Earth atmospheric scan (300-0 km from the surface, total of seven scans) at Earth limb on sunset side.
Spectra of the Moon for calibration purposes.
Observation plan
On 7 November at 00:00 UTC the Philae Lander and its instruments were initialised for observations. The lander's ROMAP instrument, and the orbiter's RPC instrument started making observations of the Earth's magnetosphere, and will continue these until 20 November.
The Closest Approach Earth pointing slot will start on 13 November at 18:00 UTC and will be concluded at 21:02 UTC. During this time frame, seven slew manoeuvres will be performed. The first of these slews (18:00-18:45 UTC) will bring the spacecraft into Earth pointing attitude. The planned observations include:
| Earth Pointing | ||
| Date/Time (UTC) | Instrument | Observation |
|
13 Nov, |
OSIRIS | Earth night-side targeted pointing: search for Leonids events in the Earth's atmosphere + images of urban regions |
|
13 Nov, 20:01 - 20:37 |
VIRTIS | Study of fluorescence emission of CO2 and O2 through Earth atmospheric scan (300-0 km from the surface, total of 7 scans) at limb on sunset side |
| 13 Nov, 20:50 | Navigation camera | 15 Earth images, one every minute |
|
13 Nov, 20:52 - 21:02 |
MIRO | Test asteroid mode sequence |
| 13 Nov, 21:06 | Navigation camera | 2 Earth images, one every minute, to catch the Earth limb during the slew to Moon pointing |
The Closest Approach Moon pointing slot will start on 13 November at 21:02 UTC and will be concluded at 10:02 UTC on 14 November. Two slews will be performed in this time frame; the first one (13 November, 21:02 UTC - 22:02 UTC) will change Rosetta's attitude to be Moon-pointing. The second slew (14 November, 08:32 UTC - 10:02 UTC) will conclude the Closest Approach Moon pointing slot. The planned observations include:
| Moon Pointing | ||
|
Date/Time (UTC) |
Instrument | Observation |
|
13 Nov, 22:02 |
ALICE | Centre of illumination of the Moon |
|
13 Nov |
OSIRIS | Spectro-photometry of the Moon from different viewpoints |
| 13 Nov, 23:00 | Navigation camera | 10 Moon images, one every five minutes, taken from a distance between 376 781 - 377 219 km from the Moon |
|
14 Nov 03:47 - 06:17 |
ALICE | Slew scans over the Moon |
|
14 Nov 06:32 - 07:32 |
OSIRIS | Spectro-photometry of the Moon from different viewpoints |
|
14 Nov 06:32 - 08:32 |
ALICE | Centre of illumination of the Moon (90° phase angle) |
After closest approach, the ROMAP and RPC observations of the Earth magnetosphere will be on-going. Other planned observations include:
| After closest approach | ||
|
Date/Time |
Instrument | Observation |
|
15 Nov, 01:05 - 02:00 |
OSIRIS | Spectro-photometry of the Moon |
|
15 Nov, 02:30 - 03:00 |
OSIRIS |
Earth global imaging, from a distance of |
|
15 Nov, 02:41 - 02:53 |
Navigation camera | 9 images of the Earth (the Moon is not in the field of view), one every minute from 02:41 UTC until 02:43 UTC, and from 02:48 until 02:53 UTC. The images are taken from a distance between 1 019 569 and 1 026 340 km |
|
16 Nov, |
OSIRIS | Distant imaging of the Earth-Moon system |


